Recently Diagnosed or Relapsed? Stop Looking For a Miracle Cure, and Use Evidence-Based Therapies To Enhance Your Treatment and Prolong Your Remission
Multiple Myeloma an incurable disease, but I have spent the last 25 years in remission using a blend of conventional oncology and evidence-based nutrition, supplementation, and lifestyle therapies from peer-reviewed studies that your oncologist probably hasn't told you about.
Click the orange button to the right to learn more about what you can start doing today.
- You are here:
- Home »
- Blog »
- Multiple Myeloma »
- Multiple Myeloma Side Effects- Resolving Blood Clots
Multiple Myeloma Side Effects- Resolving Blood Clots
“After the cancer itself, blood clots are the second leading cause of death, along with infection, in real-world cancer outpatients receiving chemotherapy…
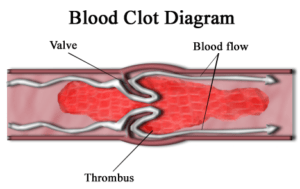
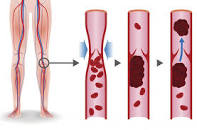
I was diagnosed with multiple myeloma (MM) in early 1994. One of the many multiple myeloma side effects that I developed was a blood clot aka deep-vein thrombosis.
A blood clot (DVT) can be either a symptom of MM, or a serious side effect of chemotherapy. Newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (MM) patients must understand the risks of short, long-term and late stage side effects caused by chemotherapy if they are to be able to prevent and possibly heal these side effects.
After dying from your multiple myeloma itself, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) aka blood clots, is the second leading cause of dealth among patients receiving chemotherapy according to the article linked and excerpted below.
I developed a DVT in my left leg about a month after I began my first course of a chemo cocktail called V.A.D. I underwent the standard-of-care therapy for blood clot prevention for about six months after my DVT diagnosis. However I eventually decided that I ran the risk of a number of long-term side effe
I discoved that supplements such as nattokinase did a good job of dissolving DVT’s with no side effects. Further, I made changes to my diet that reduce my future risk of getting another blood clots.
The first article linked and excerpted below, in my opinion at least, equivocates as to the benefit of standard-of-care oral anticoagulants like Xarelto. So I guess I’ll keep taking nattokinase, Wobenzyme, omega-3 fatty acids, others.
The second article linked below explains the changes I made to my diet.
- Adding water, juices, etc. to your daily diet is easy
- I don’t drink grape juice. I drink approx. 3 glasses of red wine weekly and I supplement with resveratrol
- My wife and I eat a lot of pasta for dinner. Garlic and red wine are the key to pasta in my opinion…
- I used to eat donuts, fried foods, etc. No longer. But this change took me awhile. You can do it too…
- Olive oil (phenols) inhibit MM. Olive oil inhibits blood clots. See pasta above. Enough said
- Leafy greens contain vitamin K2. Vitamin K2 inhibits multiple myeloma.
- Animal fat, trans fat, all increase your risk of blood clots.
My point is that DVT is a nasty side effect of chemotherapy and you, the MM patient, have several options to reduce your risk of blood clot.
Scroll down the page to post a question or comment if you would like to learn more about non-toxic therapies to manage DVT’s.
Dissolving my DVT was related to developing chronic atrial fibrillation which raises my risk of stroke. There are lots of things for us to discuss.
Thanks,
David Emerson
- Multiple Myeloma Survivor
- MM Cancer Coach
- Director PeopleBeatingCancer
Recommended Reading:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis aka Blood Clots In Multiple Myeloma
- Multiple Myeloma Chemos That Cause Kidney Damage
- VTE Blood Clot Treatment Dissatisfaction
- Reduce Cardiovascular and Thromboembolic Mortality Risk in Myeloma
Rivoraxaban Fails to Reduce VTE Incidence During Trial Period
“Treatment with rivaroxaban did not significantly decrease incidence of venous thromboembolism or death from VTE in a 180-day trial period, according to results of the phase 3b randomized trial CASSINI published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
However, rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Janssen) — an oral, highly selective direct inhibitor of factor Xa — did lead to substantially lower incidences of VTE and death during the intervention period.
“After the cancer itself, blood clots are the second leading cause of death, along with infection, in real-world cancer outpatients receiving chemotherapy, and a major cause of morbidity, mortality and increased costs among patients hospitalized with a blood clot,”
“The results of this study will help us understand how we should weigh the potential benefits of reducing blood clots with potential risks, and how to establish a standard for assessing which [patients with] cancer are at the highest risk [for] developing blood clots.”
Although ambulatory patients undergoing systemic cancer therapy are at risk for VTE, whether thromboprophylaxis benefits these patients is uncertain.
Researchers randomly assigned 841 ambulatory patients (median age, 63 years; range, 23-88; 50.9% men; 83% white) with cancer and without deep-vein thrombosis to receive 10 mg rivaroxaban (n = 420) or a placebo (n = 421) daily for up to 180 days. Screening took place every 8 weeks…
A composite of confirmed proximal DVT in a lower limb, pulmonary embolism, symptomatic DVT in an upper limb, distal DVT in a lower limb, or death from VTE, through day 180, served as the primary efficacy endpoint. Major bleeding served as the primary safety endpoint.
The mean intervention period was 4.3 months and ranged from the first dose to the last dose plus 2 days…
Death of any cause up to 180 days — a second efficacy endpoint — occurred among 84 patients in the rivaroxaban group and 100 in the placebo group (20% vs. 23.8%;)
Researchers also conducted a prespecified supportive analysis of the same endpoint during the intervention period. Results showed the primary endpoint occurred in 11 patients in the rivaroxaban group and in 27 in the placebo group (2.6% vs. 6.4%; HR = 0.4; 95% CI, 0.2-0.8) during the intervention period.
Eight patients in the rivaroxaban group and four in the placebo group experienced major bleeding (2% vs. 1%; HR = 1.96; 95% CI, 0.59-6.49)…
“There’s a longstanding need for the oncology and hematology communities to address this issue holistically and understand the true burden blood clots and related conditions and hospitalizations have on [patients with] cancer,””
7 Diet Tips to Help Prevent Deep Vein Thrombosis
“1) Drink Up to Keep Blood Flowing Smoothly
Dehydration can cause your blood to thicken, increasing your risk for a blood clot. To stay well-hydrated, women should consume an average of 91 ounces (oz) of water from all beverages and food daily, and men an average of 125 oz, according to the National Academy of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine guidelines.
One way to gauge if you’re on track is to check your urine. If it is a pale yellow color or clear, you are probably drinking enough, according to the Cleveland Clinic. If it’s amber-colored or darker, you’re probably not and should increase your daily water intake.
2) Sip Grape Juice or Red Wine to Make Platelets Less Sticky
Drinking moderate amounts of red wine or purple grape juice daily helps keep blood platelets from sticking together and forming clots, thanks to powerful antioxidants called polyphenols in purple grapes, suggested a review of previous studies, published in The Journal of Nutrition.
3) Flavor Food With Garlic to Stop Trouble Before It Starts
Garlic is thought to have many health benefits, including possibly breaking up potentially harmful clusters of platelets in the bloodstream, according to research published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. The best way to reap that benefit from garlic, the research shows, is to crush the raw cloves to release their beneficial compounds, then eat them raw, oven-roasted, or boiled for three minutes or less.
4) Avoid Unhealthy Fats to Avoid Slowing Circulation
The same foods that in excess can cause plaque buildup in blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart disease, can also increase the risk of developing DVT, Dr. Masley notes. That means you want to stay away completely from unhealthy trans fats and cut way back on the saturated fats in full-fat dairy and fatty cuts of red meat, as well as sugar and salt, according to the American Heart Association. “These are all foods that increase inflammation,” Masley explains…
5) Use Virgin Olive Oil to Cut Your Blood Clot Risk
Similarly, an earlier study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that antioxidants called phenols in virgin olive oil helped prevent blood clots. In the study, people who consumed virgin olive oil with a high phenol content had lower levels of a substance that promotes blood clots…
6) Make Leafy Greens a Routine
Leafy greens contain vitamin K2. Vitamin K2 inhibits multiple myeloma.
7) Limit Animal Fats in Your Diet
Finally, Masley says that the same foods that are bad for cardiovascular health in general can also increase your risk of developing blood clots. That means you want to stay away from unhealthy trans fats, from the saturated fats in full-fat dairy and fatty meats, and from all types of sugar. “These are all foods that increase inflammation,”