Diagnosed with Cancer? Your two greatest challenges are understanding cancer and understanding possible side effects from chemo and radiation. Knowledge is Power!
Learn about conventional, complementary, and integrative therapies.
Dealing with treatment side effects? Learn about evidence-based therapies to alleviate your symptoms.
Click the orange button to the right to learn more.
- You are here:
- Home »
- Blog »
- Newly Diagnosed »
- Cord-Blood Transplantation- Side Effects
Cord-Blood Transplantation- Side Effects

“Researchers have identified a new diarrheal syndrome that affects patients who have undergone cord-blood hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation”
I had an an autologous stem cell transplant at the end of 1995. A stem cell transplant, in general, is a remarkable medical achievement. As always, the devil is in the details as they say.
Please don’t undergo a complicated medical procedure without first understanding its risks and benefits. I followed my oncologist’s instructions without ever asking a single question. Big mistake.
The different types of transplants are:
- Autologous stem cell transplantation (your own stem cells)
- Allogeneic stem cell transplantation (donor stem cells)
- Cord-blood stem cell transplantation (cord blood stem cells)
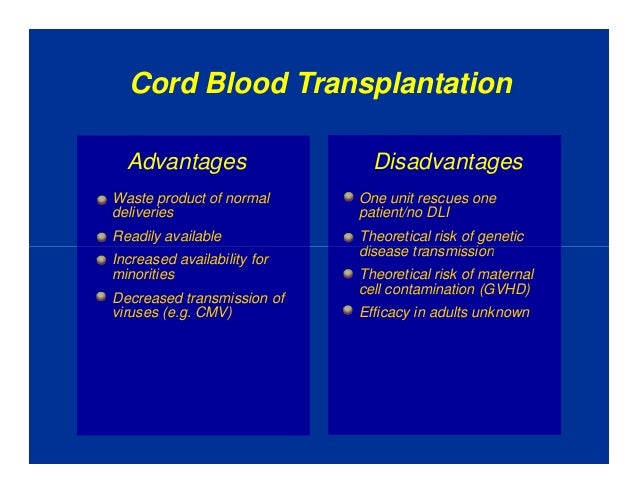
A cord-blood hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation is a complicated procedure with real risks and benefits. The key is to learn about complications and ways to combat those side effects and complications.
Have you undergone a cord blood stem cell transplant? What complications have you experienced? Please scroll down the page, post a question or comment and I will reply ASAP.
thank you
David Emerson
- Cancer Survivor
- Cancer Coach
- Director PeopleBeatingCancer
New Diarrheal Syndrome Tied to Cord-Blood Transplants
“Researchers have identified a new diarrheal syndrome that affects patients who have undergone cord-blood hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation..
It is important to distinguish the new syndrome, which they call “cord colitis syndrome,” from other causes of diarrheal illness that have a similar initial presentation in this patient population – notably graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) – because treatment differs. Cord colitis syndrome responds rapidly to antibiotic therapy but tends to relapse when treatment stops, so a prolonged course is often necessary…
Severe diarrhea following hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) can almost always be traced to a variety of sources. Acute GVHD is perhaps the most well-recognized. Classic viral causes include cytomegalovirus and adenovirus, but more common pathogens such as rotavirus and norovirus are being recognized more frequently. Epstein-Barr virus can incite lymphoproliferative disease involving the gut, which produces diarrhea. And protozoal infections from giardia and cryptosporidium have been reported.
In addition, mucositis and neutropenic enterocolitis induced by conditioning regimens frequently cause diarrhea, as do Clostridium difficile infection and long-term medications, the investigators said…
The median patient age was 48 years (range, 19-67 years). The patients underwent cord-blood HSCT to treat numerous underlying diseases including acute myeloid leukemia (35%), non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (22%), myelodysplastic syndrome (10%), Hodgkin’s disease (8%), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (7%), and aplastic anemia (7%)…
Stool samples were negative for all bacterial, viral, fungal, protozoal, and parasitic organisms as well as toxins that were tested for. Nevertheless, patients showed a rapid response to empiric antibiotic therapy – usually metronidazole, either alone or in combination with a fluoroquinolone…
The investigators found no correlation between the cord colitis syndrome and factors such as patient age or race, the underlying hematologic disease, the conditioning regimen, or the regimen to prevent GVHD.”
Infectious Complications After Umbilical Cord Blood Transplantation for Hematological Malignancy
“Background- Umbilical cord blood transplant (UCBT) is used for patients who do not have a matched donor, but engraftment often takes longer than with a standard allogeneic transplant, likely increasing the risk for infection. We characterized specific infections and outcomes in adults undergoing UCBT at our 2 centers.
Infectious complications were common after UCBT, especially in the first 30 days. Deaths from viral infections were fewer than expected. Delayed engraftment and nonengraftment continue to convey increased risk for fatal bacterial and fungal infections post-UCBT…’