Diagnosed with Cancer? Your two greatest challenges are understanding cancer and understanding possible side effects from chemo and radiation. Knowledge is Power!
Learn about conventional, complementary, and integrative therapies.
Dealing with treatment side effects? Learn about evidence-based therapies to alleviate your symptoms.
Click the orange button to the right to learn more.
- You are here:
- Home »
- Blog »
- Skin Cancer »
- Tanning and Skin Cancer- How Can I Tell?
Tanning and Skin Cancer- How Can I Tell?

Melanoma Versus Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. What’s the Difference? How Can I Tell if a Mole is a Problem?
Ironically tanning makes you look healthier. As a teen I sat in the sun as often as I could. I thought that girls would find me more attractive if I had a tan. Sometimes I even spread tin foil over a double record album to reflect the U.V. rays up to my face.
And now? I study each and every mole on my 60 plus year old body to see if the mole has changed- grown larger, darker, just changed.
I wish I knew then what I know now…
Self-examination is important as far as it goes. Keep in mind however that the two most effective ways to determine if a mole is skin cancer are to:
- Have your dermatologist examine you with a dermoscope–
- Learn about and pursue evidence-based, non-toxic therapies to reduce your risk of skin cancer-
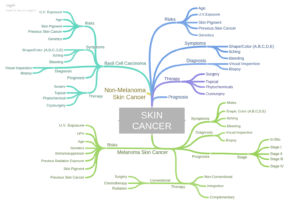
Click the image below to learn more about skin cancer-
1) Melanoma-“Melanoma is less common than other skin cancers. However, it is much more dangerous if it is not found in the early stages. It causes the majority (75%) of deaths related to skin cancer..”
2) Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer– “They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body.[1] There are three main types: basal cell cancer (BCC), squamous cell cancer (SCC) and melanoma.[2] The first two together along with a number of less common skin cancers are known as nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC)”
I am both a cancer survivor and cancer coach. I live an evidence-based, non-toxic, anti-cancer lifestyle through nutrition, supplementation, detox, etc. therapies.
To learn more about other evidence-based therapies that can help prevent the development of non-melanoma skin cancer or relapse, please watch the short video below:
To learn more scroll down the page and ask me a question. About a melanoma or non-melanoma skin cancer diagnosis, about anti-skin cancer supplementation, you name it, let’s talk about it.
thanks
David Emerson
- Cancer Survivor
- Cancer Coach
- Director PeopleBeatingCancer
7 Common Tanning and Sun Exposure Myths, Busted
Plenty of people think they need to get a base tan to avoid getting a sunburn on vacation, but this is a mistake according to Dr. Madeliene Gainers of Anne Arundel Dermatology in Florida.
“A tan in and of itself is evidence of skin damage,” she told Healthline. “The skin appears darker because it redistributes melanin in an effort to protect itself.”
But it’s not just skin damage that occurs. DNA damageTrusted Source also takes place during tanning…
If you live in a northern state where sun tends to be limited in the winter months, you’ve probably heard it’s a good idea to use a tanning bed to keep your vitamin D levels where they need to be.
But that’s simply not so, according to Gainers.
“There’s no reason to damage the skin, putting oneself at risk for skin cancer as well as accelerated aging, to get vitamin D. Achieving adequate vitamin D levels can be accomplished through proper diet and supplementation without harming the skin,” she said…
Fair-skinned people tend to realize it’s best for them to avoid sun exposure. But it’s a common myth that those with darker skin don’t need to take the same precaution.
Dr. Karyn Grossman of Grossman Dermatology in Santa Monica and New York City agreed that any tan at all indicates damage to the genetic code of your skin…
We get it: You feel like you look better with a tan. But you don’t need to put your skin at risk in order to achieve those results.
“Some people believe you have to get a true suntan to have tan skin,” Gainers said, noting it isn’t true. “Nowadays there are several effective, natural-appearing sunless tanners and bronzers. There’s no reason to damage your skin if you want the look of having a tan.”..
There are two different types of UV rays: UVA and UVB rays. UVB rays tend to get the bad rap, as they are associated most with sunburns and skin cancer development. But that doesn’t mean UVA rays are safe.
“UVA rays are more related to photoaging, such as wrinkling and irregular texture,” Lin explained. “UVB rays are linked to skin cancer. Neither are desirable.”…
Many people have known at least one person who’s had a skin cancer scare. And in many cases, they may have walked away with nothing more than a small scar. But it’s important to know just how deadly skin cancer can be.
“One in five Americans across all ethnicities will get skin cancer,” Grossman said. And not all of those people will survive. “One person dies from skin cancer every hour in the United States.”…
In case it wasn’t already clear, any tan whatsoever can set you up for future skin problems.
“Acute sunburns are painful and and may increase the risk of melanoma,” Lin said. “But tanning cancause photoaging and predispose you to skin cancer.”
The problem is that most people ignore those future risks because they can’t see them today…”
Warning: That Tan Could Be Hazardous
“For decades, researchers saw indoor tanning as little more than a curiosity. But a review of the scientific evidence published last year estimated that tanning beds account for as many as 400,000 cases of skin cancer in the United States each year, including 6,000 cases of melanoma, the deadliest form…
Last year, the surgeon general called on Americans to reduce their exposure to the sun and tanning beds to prevent skin cancer, and the Food and Drug Administration invoked its most serious risk warning, lifting tanning beds from a category that included Band-Aids to that of potentially harmful medical devices…
Dr. Jeffrey E. Gershenwald, a leader of the melanoma Atlas project, said studies to date showed that a majority of melanomas initially arising on the skin contain mutations associated with ultraviolet exposure. As for burning, one recent study controlled for that, and still found an increased risk from indoor tanning…
Experts say the increase is real, and not just a matter of better detection. Thicker, more dangerous tumors are rising just as fast — particularly among young women — and rates are also up among the uninsured, who would be less likely to get medical checkups…